Determining the internal resistance Maximum Power of a Cell

Objective
1- To determine the internal resistance of an electrolytic cell.
2- To determine the electromotive force (EMF) of the cell.
3-To find the maximum power the cell can supply.
4-study the relationship between the voltage and current of the cell under different loads.
Equipment
● Battery or cell
● Voltmeter
● Ammeter
● Variable resistor ● Switch
Method
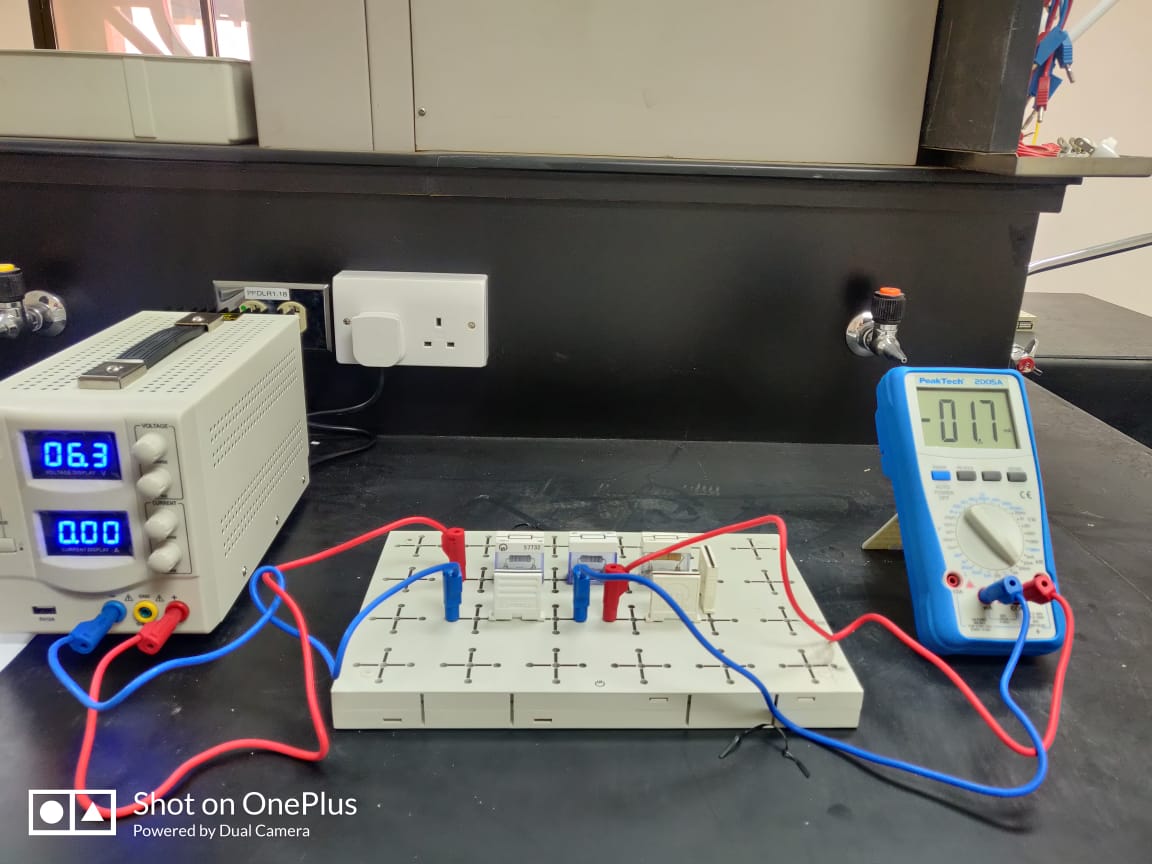
1. Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram.
2. Set the variable resistor to its maximum value.
3. Close the switch and record voltage from the voltmeter and the current from the ammeter, open the switch between readings to prevent heating of the variable resistor.

4. Decrease the resistance of the variable resistor and repeat this, obtaining pairs of readings of V and I over the widest possible range as in table below.
5. Calculate the power supplied by the battery for each current value by using P = VI and also calculate the resistance at each current value by R = V/I.
Data table
Experiment: Determining the Internal Resistance and Maximum Power of a Cell
Enter Measurements:
| Voltage (V) | Current (I) | Power P = VI (W) | Resistance R = V/I (Ω) |
|---|
V vs I Graph
Power vs Resistance Graph
Scientific Explanation
This experiment is based on the relationship:
V = ε − Ir
Where:
ε = Electromotive Force (EMF) of the cell
r = Internal resistance
When the external resistance changes, the current changes, and therefore the voltage V changes.
Plotting V against I produces a straight line:
• Slope = −r (negative internal resistance)
• Intercept = ε (EMF of the cell)
The Power vs Resistance curve shows a peak at:
R = r
Which is the Maximum Power Transfer Condition.