Half Wave Rectifier
Objectives
To calculate, compare, draw, and measure the DC output voltages of half-wave.
To recognize a half-wave rectified sinusoidal voltage.
To understand the effect of a reservoir capacitor upon the rectified waveform
Theory
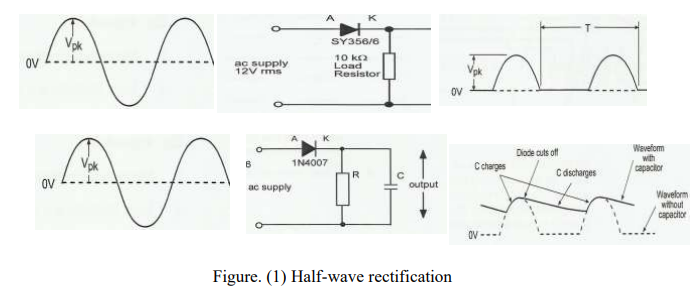
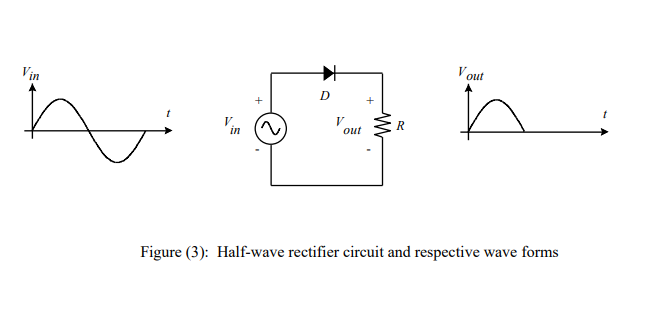
The conversion of alternating voltage (changes its direction) to directed voltage. This conversion is called rectification. To achieve the rectification of alternating voltage you must to use some circuit. The simplest one is the half-wave rectifier in which a single diode is used, see Fig. 1.
For a sinusoidal waveform the diode passes a current at first part 1 of waveform, because it forward-biased. At the same time the diode doesn’t pass a current for second part 2, because it reverse-biased. In this case only the half of the input waveform passes through the diode. The output voltage (rectified waveform) changes with time which makes it unestablish with time. To produce a steady output directed voltage and free from variations the load resistor is connected in parallel with capacitor
Apparatus
1- Breadboard or Rastered socket panel, DIN A4.
2- Oscilloscope.
3- AC Power Supply (0-12V).
4- AC Voltmeter.
5- DC Voltmeter.
6- Si diode (1N4007).
7- Resistor 10kΩ.
8- 5 different capacitors (0.47µF, 4.7µF, 47µF, 100µF, 470µF).
9- Connecting wires.
10- Set of bridge plugs.
Procedure
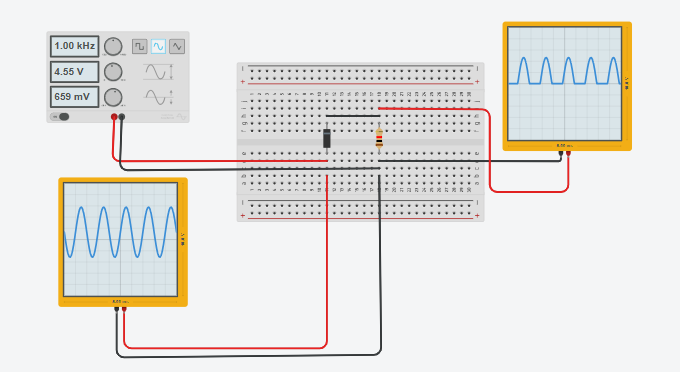
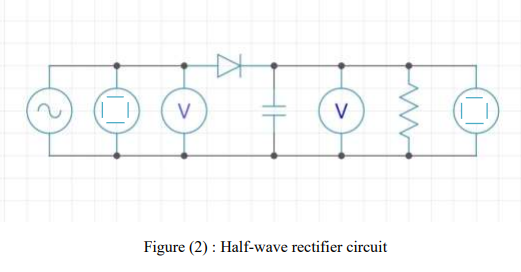
1- Connect the circuit as shown in figure (2), Do not connect the capacitor.
2- Keeping the input AC voltage at a certain value (Vin=5V).
3- Determine the DC output voltage (Vout) of the rectifier circuit by DC Voltmeter.
4- Draw and label the parts of the input and the output wave form as viewed from the oscilloscope.
5- Add a one capacitor in the circuit and Determine in each time (Vout) and (output wave form).
6- Describe the viewed output wave form.
7- Determine the threshold voltage Vth and Vavg
Circuit Diagram
Data Sheet
Without a Capacitor Table (1)
| Output wave DC | Output wave DC | Input wave AC | Input wave AC |
|---|---|---|---|
| (V) Vout | (V)Vin | ||
| Vp out (V) | (V) Vp in | ||
| Wave form | Wave form | ||
| Vth=Vp in-Vp out | Vavg=Vpin/3.14 |
With a Capacitor Table (2)
| C (μF) | ||||||
| Vout DC (V) | ||||||
| Wave form |